
#EXCEL VBA ON ERROR GOTO ERRORHANDLER CODE#
Sub YourMethodName()Įxit Sub 'The exit sub line is essential, as the code will otherwise
Thus, it is best practice for function and readability to place error handlers at the end of a code block.

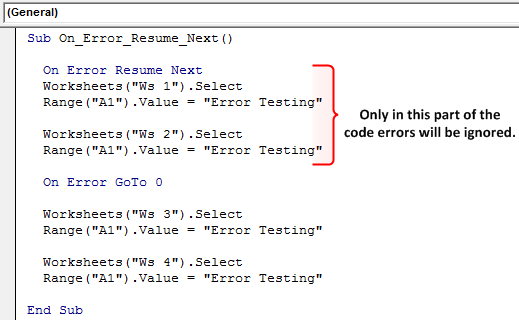
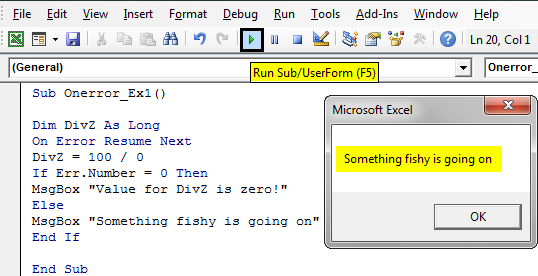
Note: It is essential that the Exit Sub line is placed above the first error handler and before every subsequent error handler to prevent the code from naturally progressing into the block without an error being called. The subroutine below demonstrates the syntax of an On Error GoTo call. Multiple error handling blocks can be used by making different calls of On Error GoTo. The tag can be filled with any string (including numeric strings), and will send the code to the corresponding string that is followed by a colon. This allows the programmer to control exactly how VBA handles an error by sending the code to the specified line. This method of error handling is recommended for all code that is distributed to other users. Note: It is also a best practice to immediately reset the error handler as soon as you no longer need the On Error Resume Next call Thus, On Error Resume Next was necessary to avoid creating two instances of the application. Had we not used the On Error Resume Next call and the Powerpoint application was not already open, the GetObject method would throw an error. Set PPApp = CreateObject("PowerPoint.Application") Set PPApp = GetObject(, "PowerPoint.Application") 'Open PPT if not running, otherwise select active instance For example, when launching a separate program from an Excel Macro, the On Error Resume Next call can be useful if you are unsure whether or not the program is already open: 'In this example, we open an instance of Powerpoint using the On Error Resume Next call In very specific instances, this line can be useful, but it should be avoided outside of these cases. On Error Resume Next will cause VBA to ignore any errors that are thrown at runtime for all lines following the error call until the error handler has been changed. While writing code, this method is the simplest and most useful, but it should always be avoided for code that is distributed to end users, as this method is very unsightly and difficult for end users to understand. In this mode, any runtime errors will launch the typical VBA error message, allowing you to either end the code or enter debug mode, identifying the source. If no error handling is set in your code, On Error GoTo 0 is the default error handler. Prefer using: On Error GoTo 'Prefer using There are three main methods of Error Handling in VBA, two of which should be avoided for distributed programs unless specifically required in the code. Good error handling prevents end users from seeing VBA runtime errors and helps the developer easily diagnose and correct errors. WorksheetFunction object executes faster than a UDF equivalent.Switch off properties during macro execution.Avoid using ActiveCell or ActiveSheet in Excel.Avoid re-purposing the names of Properties or Methods as your variables.Always define and set references to all Workbooks and Sheets.Use Worksheet object and not Sheet object.Methods for Finding the Last Used Row or Column in a Worksheet.Loop through all Sheets in Active Workbook.Creating a drop-down menu in the Active Worksheet with a Combo Box.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
